Mastering the Art of 7018 Stick Welding: A Comprehensive Guide
americanindustrialsupl and its partners may earn a commission if you purchase a product through one of our links.
7018 stick welding encapsulates a blend of skill, precision, and the right knowledge of equipment and materials. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or a novice, mastering the 7018 electrode can lead to stronger, more resilient welds in a myriad of applications.
Key Takeaways
- 7018 electrodes offer high tensile strength and versatility across various positions.
- Proper electrode storage prevents moisture uptake and ensures weld integrity.
- A tight arc and correct amperage settings are key for optimal welding performance.
Part One: Understanding 7018 Stick Welding:

When you delve into the world of 7018 stick welding, you’re engaging with a technique revered for its robustness and versatility. The 7018 electrode stands out as a central component in this process.
Characteristics of the 7018 Electrode
The 7018 electrode a type of low hydrogen electrode generally used in shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) .It is notable for its impressive tensile strength of 70,000 psi. This strength makes it a go-to choice for demanding welding tasks. Its unique composition includes a low-hydrogen iron powder coating. This special coating plays a crucial role in the electrode’s performance but requires you to store it meticulously to prevent moisture absorption. If moisture creeps in, it can significantly deteriorate the weld’s integrity.
Decoding the Numbers on the Electrode
Understanding the coding on a E7018 electrode unlocks insights into its capabilities. Here’s a breakdown:
| Number | Meaning | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| 70 | Tensile Strength | A tensile strength of 70,000 psi, signifying the electrode’s robustness. |
| 1 | Positional Flexibility | Suitable for all welding positions, although it’s less ideal for downward slopes. |
| 8 | Flux Composition | Indicates a low-hydrogen flux with additives like potassium and iron powder, enhancing the weld quality. |
Incorporating these elements into your welding practice with 7018 electrodes can lead to enhanced outcomes in various applications. From structural steel fabrication to repair work, understanding and utilizing the properties of the 7018 electrode can make a significant difference in your welding projects.
Specifications and Applications of 7018 Electrodes: A Detailed Overview
The 7018 electrode, with its unique iron powder low hydrogen flux composition, is a key player in the realm of stick welding, especially in industrial settings. This electrode is highly valued for its capacity to create welds that resist cracking, a crucial quality in high-stress environments.
Detailed Specifications of 7018 Electrodes
| Specification | Detail | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Flux Composition | Iron Powder Low Hydrogen | Ensures strong, durable welds, reducing the risk of weld failure under stress. |
| Crack Resistance | High | Ideal for projects where structural integrity is paramount. |
| Welding Positions | All Positions (except downward slopes) | Versatile for various welding angles, increasing applicability. |
Key Uses in Industrial Projects
The 7018 electrode finds its niche in several high-demand applications, where its properties are particularly beneficial:
- Pipe Welding: In the world of pipeline fabrication and repair, the 7018 electrode is a preferred choice. Its strong, resilient welds are essential in pipelines, which often operate under high pressure and are exposed to various environmental conditions.
- Pressure Vessel Construction: For manufacturing pressure vessels, the integrity of each weld is critical. The 7018 electrode’s crack-resistant nature ensures the reliability of these vessels, which are often used in industries like petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals.
- Construction and Infrastructure: In construction, especially when dealing with structural steel, the 7018 electrode’s ability to produce sturdy, long-lasting welds is invaluable. Its usage spans from building frameworks to bridge construction, underscoring its role in ensuring public safety and structural durability.
- Repair Work: The 7018 electrode is not just limited to new constructions; it’s equally adept in repair work. Its compatibility with various metals and crack-resistant welds makes it a top choice for maintenance and restoration projects.
Mastering Techniques for Using the 7018 Rod: Key Strategies and Practices
Utilizing the 7018 rod effectively involves understanding and applying specific techniques tailored to its unique properties. The 7018 rod is known for its drag technique, a high deposition rate, and a tendency to form slag. These characteristics necessitate maintaining a tight arc and being vigilant about the arc distance. Developing proficiency in these techniques is best achieved through consistent practice.
Core Techniques for the 7018 Rod
| Technique | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Drag Technique | Involves dragging the rod along the weld joint. | Provides better control and penetration, ideal for thicker materials. |
| High Deposition Rate | The rate at which the electrode material is deposited on the workpiece. | Enables quicker welds, suitable for projects requiring speed and efficiency. |
| Slag Formation Management | Skillful handling of slag, a byproduct of welding. | Essential for maintaining weld quality and preventing defects. |
Managing Arc and Distance
Proper management of arc length and distance is critical when using the 7018 rod. Here’s a guideline:
| Aspect | Strategy | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Tight Arc | Keeping the arc short and consistent. | Results in a stable welding pool, minimizes spatter, and enhances weld quality. |
| Arc Distance | Monitoring and adjusting the distance between the electrode and the workpiece. | Ensures optimal heat input and prevents defects like undercutting or excessive penetration. |
Practice for Perfection with 7018 Stick Welding
Regular practice is key to mastering these techniques. It’s advisable to work on various projects, experimenting with different thicknesses and joint types. This hands-on experience allows you to understand how slight adjustments in technique can significantly impact the outcome of your welds.
Optimizing Fillet Welds with the 7018 Electrode: Techniques and Best Practices
When it comes to fillet welding, the 7018 electrode is an excellent choice, particularly for achieving strong and aesthetically pleasing results. The key to successful fillet welding with the 7018 lies in managing the weld pool and overlapping weld passes effectively.
Techniques for Fillet Welding with 7018
| Technique | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Pool Management | Keeping the weld pool close to the metal’s edge. | Ensures proper fusion at the root and sides of the fillet, enhancing the strength and appearance of the weld. |
| Overlapping Passes | Methodically overlapping welding passes. | Creates a uniform and smooth weld bead, improving both structural integrity and visual appeal. |
Best Practices for Fillet Welding with the 7018
- Angle and Speed: Maintain an optimal angle of about 45 degrees to the workpiece. Adjust your travel speed to ensure a consistent weld pool size, which is crucial for uniform fillet welds.
- Electrode Manipulation: Use a slight side-to-side or whipping motion to evenly distribute the weld metal and ensure thorough fusion along the joint.
- Heat Input Management: Carefully control the heat input to avoid distortions, particularly in thinner materials. This involves adjusting the amperage settings according to the thickness of the metal.
- Layering Technique: For thicker fillet welds, employ a multi-layer technique. Start with a root pass and then build subsequent layers, ensuring each layer fuses well with the previous one.
Effective Storage Strategies for 7018 Electrodes: Ensuring Quality and Longevity

For 7018 electrodes, appropriate storage is not just a recommendation, it’s a necessity. The unique composition of these electrodes demands specific conditions to maintain their integrity and performance. Understanding and implementing proper storage techniques is crucial in preventing weld defects caused by compromised electrodes.
Key Storage Methods and Temperatures for 7018 Electrodes
| Storage Aspect | Method/Condition | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Maintaining a temperature range of 250-300°F (121-149°C). | Preserves the low-hydrogen characteristics and prevents moisture absorption. |
| Environment | Dry and controlled humidity. | Reduces the risk of moisture exposure that can induced defects in the electrodes. |
| Container Type | Air-tight and moisture-resistant containers. | Ensures a stable environment, free from external humidity and contaminants. |
Detailed Guidelines for Optimal Storage
- Temperature Regulation: Utilize specialized ovens or storage containers capable of maintaining the recommended temperature range. Regularly check and calibrate these storage units to ensure consistent temperature control.
- Humidity Control: In areas with high humidity, it’s essential to use dehumidifiers or sealed storage spaces to keep the air around the electrodes dry.
- Electrode Rotation: If you have a large stock of 7018 electrodes, practice a ‘first in, first out’ rotation system. This ensures that no batch of electrodes stays in storage longer than necessary, reducing the potential for quality degradation over time.
- Reconditioning: If electrodes have been exposed to moisture or have been stored for an extended period, recondition them by heating at the higher end of the recommended temperature range for several hours before use.
Part Two: Advanced Welding Techniques and Settings
Mastering Vertical Stick Welding with 7018 Electrodes: Techniques and Settings
Vertical stick welding, particularly with 7018 electrodes, demands precision in technique and settings. This welding position, characterized by its vertical direction, requires specific considerations to ensure effective and strong welds.
Key Considerations for Vertical Welding with 7018
- Amperage Settings: The choice of amperage is crucial in vertical welding to prevent the electrode from sticking while also maintaining a stable and controlled arc. For a 1/8″ 7018 rod, an amperage around 115 amps is typically effective, especially for thicker materials.
- Uphill vs. Downhill Welding: The 7018 electrode is well-suited for vertical uphill welding, where the welder moves the electrode upwards along the joint. This method allows for better control over the weld pool and deeper penetration. In contrast, vertical downhill welding is not recommended with 7018 electrodes due to their basic or low-hydrogen characteristics. Downhill welding tends to be faster but can compromise penetration and weld quality in this context.
Detailed Guidelines for Vertical Stick Welding with 7018
| Aspect | Strategy | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Arc Control | Maintain a tight and consistent arc length. | Ensures a stable arc and better penetration, critical in vertical positions. |
| Electrode Angle | Hold the electrode at a slight angle. | Facilitates better control of the weld pool and bead shape. |
| Travel Speed | Adjust speed to suit the thickness of the material and heat input. | Controls the weld bead size and appearance, preventing sagging or thinning of the weld. |
| Rod Selection | Choose the appropriate rod diameter for the material thickness. | Optimizes weld quality and ease of handling. For example, thinner materials may require a smaller diameter rod. |
Overhead Welding with 7018 Stick Welding
Overhead welding poses unique challenges, especially with slag. When using a 7018 electrode, the key is to maintain a tight arc and angle the electrode slightly away from the direction of welding to control the slag flow. Amperage should be adjusted to ensure the puddle is manageable and not too fluid.
Optimizing Amperage Settings for Different 7018 Electrode Diameters
In stick welding with 7018 electrodes, selecting the correct amperage is essential for achieving the best weld quality. This choice depends significantly on the diameter of the electrode being used. The appropriate amperage ensures effective melting of the electrode, proper penetration, and a stable arc, all crucial for a strong and clean weld.
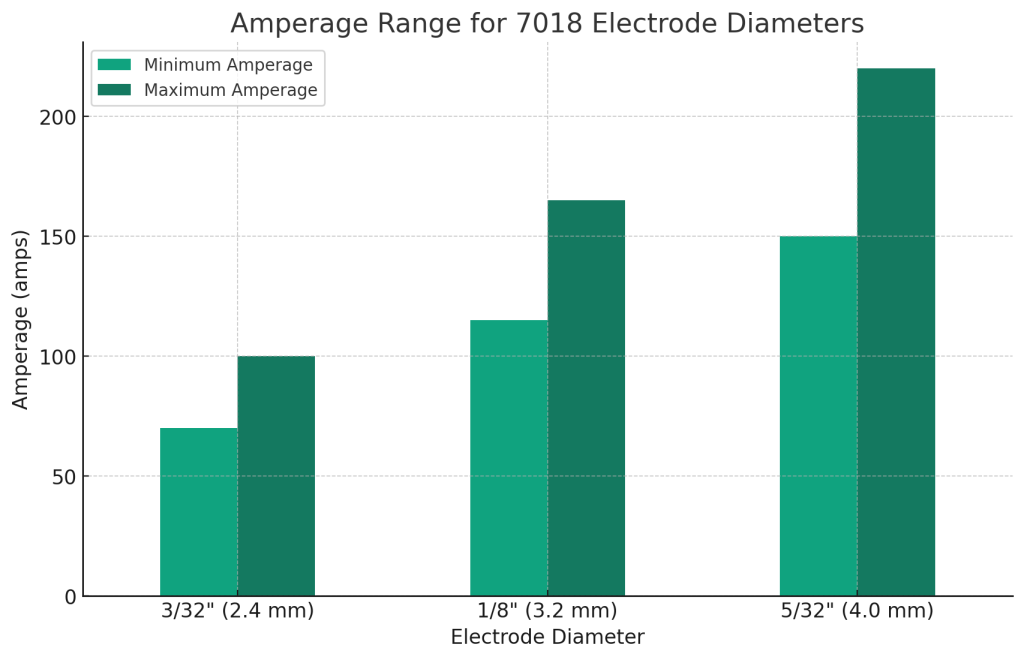
Amperage Ranges for Various 7018 Electrode Diameters
The table below provides a guide to amperage settings for different diameters of 7018 electrodes, catering to a range of welding applications:
| Electrode Diameter | Amperage Range | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| 3/32″ (2.4 mm) | 70 to 100 amps | Ideal for thin materials or fine, detailed work where lower heat input is required. |
| 1/8″ (3.2 mm) | 115 to 165 amps | Versatile for medium-thickness materials, commonly used in structural welding, repair work, and general fabrication. |
| 5/32″ (4.0 mm) | 150 to 220 amps | Suitable for thicker materials, where higher heat and deeper penetration are necessary. |
Tips for Adjusting Amperage
- Material Thickness: Consider the thickness of the material you are welding. Thicker materials generally require electrodes with larger diameters and higher amperage settings.
- Welding Position: Adjust the amperage according to the welding position. Overhead and vertical welding may require a lower amperage compared to flat or horizontal positions.
- Arc Control: A correct amperage setting helps in maintaining a stable arc and preventing issues like excessive spatter or electrode sticking.
- Practice and Experience: Experiment with different settings on scrap materials to understand how amperage affects the weld quality. This hands-on experience is invaluable in fine-tuning your welding technique.
Adjusting the amperage for 7018 electrodes is not a one-size-fits-all situation. Each material and thickness may require a specific setting to achieve the desired penetration and bead profile. Practice on scrap pieces can help determine the optimal settings for a given task.
Understanding the Interplay of Welding Position, Amperage, and Rod Size in Stick Welding
In stick welding, particularly when using 7018 electrodes, the relationship between the welding position, the size of the welding rod (electrode), and the amperage setting is crucial for achieving optimal results. Each of these factors influences the other, dictating the quality and integrity of the weld.
How Welding Position Affects Rod Size and Amperage
Different welding positions pose unique challenges and require adjustments in both the electrode size and the amperage setting. Here’s a closer look at how these elements interact:
- Overhead Welding:
- Rod Size: Typically, smaller electrodes are preferred.
- Amperage: Lower amperage settings are often used to prevent the weld pool from becoming too fluid and difficult to control.
- Outcome: These adjustments help maintain a manageable weld pool, crucial in gravity-defying overhead positions.
- Vertical Welding:
- Rod Size: Smaller electrodes can offer better control, especially in uphill welding.
- Amperage: Amperage needs to be carefully set to ensure the electrode doesn’t stick, while still allowing adequate penetration.
- Outcome: The goal is to achieve a stable arc and controlled bead formation, vital in vertical welds.
Factors Influencing the Rod Size and Amperage Choice
- Material Thickness: Thicker materials might require larger electrodes and higher amperage for deeper penetration, regardless of the position.
- Type of Joint: Certain joint designs may necessitate specific electrode sizes and amperage settings for optimal fusion and bead appearance.
- Welder’s Skill and Technique: Experienced welders might adjust these variables based on their technique and the specific demands of the welding project.
Best Practices
- Experimentation and Practice: Test different combinations of rod sizes and amperage settings on scrap material to see how they perform in various positions.
- Consultation of Guidelines: Refer to welding guidelines and standards for recommended settings based on the electrode type and welding position.
- Continuous Learning: Stay informed about the latest techniques and materials in the welding industry to refine your choices in rod size and amperage settings.
Navigating the Effects of Base Metal Temperature on Welding Amperage
In the realm of stick welding, particularly with 7018 electrodes, the temperature of the base metal plays a pivotal role in determining the appropriate welding amperage. Understanding how to adjust your welding approach based on the metal’s temperature is essential for achieving optimal weld quality and preventing common welding issues.
The Influence of Base Metal Temperature

Navigating the Effects of Base Metal Temperature on Welding Amperage
When stick welding, particularly with 7018 electrodes, the temperature of the base metal plays a pivotal role in determining the appropriate welding amperage. Understanding how to adjust your welding approach based on the metal’s temperature is essential for achieving optimal weld quality and preventing common welding issues.
The Influence of Base Metal Temperature when 7018 Stick Welding
- Low Base Metal Temperature:
- Arc Starting: Cold base metals can lead to difficulties in initiating the arc. This is due to the metal’s increased resistance to the electric current at lower temperatures.
- Amperage Adjustment: To counteract this, a slight increase in amperage might be necessary. This helps in establishing a stable arc more readily.
- Pre-Heating: In some cases, pre-heating the base metal to a specific temperature range can facilitate easier arc starting and more consistent weld quality.
- Signs of Incorrect Amperage Settings:
- Too Low Amperage: Difficulty in arc starting or maintaining a stable arc is often a telltale sign. The weld might also appear weak or poorly penetrated.
- Too High Amperage: This can lead to an excessively wide weld bead, potentially causing overheating of the base metal and issues like warping or burn-through.
Best Practices for Amperage Setting
- Material Thickness and Type: Consider the thickness and type of the base metal. Thicker and denser metals typically require higher amperage settings.
- Temperature Assessment: Evaluate the base metal temperature, especially in colder environments or with metals stored outdoors.
- Trial Runs: Conduct test runs on scrap pieces of similar material and temperature to fine-tune the amperage setting before beginning the actual welding project.
- Monitoring Weld Appearance: Pay close attention to the appearance of the weld bead and make adjustments as necessary. This is especially crucial when working in varying temperature conditions.
Strategic Guide to Purchasing 7018 Electrodes: Balancing Cost and Project Requirements
When planning to purchase 7018 electrodes for your welding projects, it’s crucial to weigh both the cost and the specific needs of your project. The price of these electrodes can fluctuate based on several factors, such as size, manufacturer, and quality. Making an informed decision ensures you get the best value while meeting the demands of your welding tasks.
Factors Influencing the Cost of 7018 Electrodes
- Electrode Size:
- The diameter and length of the 7018 electrodes can affect their price. However, the variation is typically minimal across different sizes.
- Larger electrodes might offer a better price-per-inch of welding, but it’s important to match the electrode size to the specific requirements of your project.
- Manufacturer and Quality:
- Different brands may offer electrodes at varying price points. Premium brands might command higher prices due to the perceived quality and reliability of their products.
- While cost is a factor, investing in higher-quality electrodes can result in better welds and fewer defects, which might save money in the long run.
- Bulk Purchasing:
- Buying in bulk can often reduce the cost per electrode. Consider this option if you have ongoing or large-scale projects.
- Ensure proper storage to maintain the quality of electrodes over time, especially when buying in larger quantities.
Considerations for Electrode Purchase
- Project Specifics: Assess the specific requirements of your welding project. This includes material thickness, welding position, and the desired quality of the weld.
- Welding Frequency: If you weld frequently, investing in higher-quality or bulk electrodes might be more cost-effective.
- Storage Capabilities: Ensure you have the means to store the electrodes properly, especially if purchasing in bulk. Improper storage can degrade the quality of the electrodes.
- Vendor Reliability: Choose reputable suppliers known for offering quality welding products. This ensures you get genuine and reliable 7018 electrodes.
Essential Insights on Stick Welding Polarity for 7018 Electrodes
Understanding and correctly setting the polarity is fundamental when stick welding with 7018 electrodes. Polarity in welding significantly influences arc characteristics, penetration depth, and overall weld quality. The 7018 electrodes are versatile, designed to operate efficiently with both Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current Electrode Positive (DCEP), commonly referred to as reverse polarity.
Key Points on Polarity for 7018 Electrodes
- Polarity Types:
- AC (Alternating Current): Suitable for welding magnetic materials where arc blow might be an issue. AC can be a good choice in situations where equipment only supports AC or when welding on painted or somewhat rusty materials.
- DCEP (Direct Current Electrode Positive): Preferred for most welding situations, as it provides deeper penetration and a more stable arc. In DCEP, the electrode is positively charged, attracting more electrons and delivering more heat to the weld pool.
- Impact on Welding Performance:
- Penetration Depth: Correct polarity, especially DCEP, ensures deeper penetration, essential for thicker materials or structural welding where weld strength is critical.
- Arc Stability: A stable arc, facilitated by the right polarity, contributes to better control over the weld pool and reduces issues like spatter and arc wander.
- Choosing the Right Polarity:
- Consider the material thickness and type. For example, thinner materials might not require the deep penetration offered by DCEP.
- Assess the welding environment and equipment capabilities. Some welding machines may only support a specific type of current.
Best Practices for Polarity in Stick Welding
- Equipment Check: Ensure your welding machine is correctly set for the desired polarity before starting your welding project.
- Practice Runs: Experiment with both AC and DCEP on scrap materials to understand how each affects the weld quality, especially if you’re new to using 7018 electrodes.
- Consulting Specifications: For critical projects, refer to welding specifications or guidelines that might recommend a specific polarity for certain applications or materials.
Troubleshooting Common 7018 Welding Problems
Addressing Arc Blow Issues
Arc blow can be a nuisance when stick welding, causing the arc to wander and resulting in an inconsistent weld. To mitigate this, welders can try reducing the current or changing the position of the ground clamp to minimize the magnetic field’s impact.
Resolving Welding Spatter
While 7018 electrodes are known for minimal spatter, improper technique or settings can increase its occurrence. If spatter is a problem, check your amperage and try fine-tuning the arc length. Also, ensure your electrode isn’t contaminated with moisture.
Preventing Weld Cracking
Cracking can occur due to rapid cooling or high hydrogen content. To prevent this, ensure your 7018 electrodes are properly stored to avoid moisture and follow the correct welding procedure for preheating and interpass temperatures.
Optimizing 7018 Stick Welding Performance
Achieving Optimal Weld Appearance
For welds that are as pleasing to the eye as they are strong, focus on maintaining a consistent arc length and travel speed. Practice is key to developing a steady hand that guides the electrode smoothly along the joint.
Enhancing Weld Penetration
Deep penetration is essential for the strength of the weld. With 7018 rods, using a whipping or slight side-to-side motion can help achieve better penetration, especially in thicker materials.
7018 Stick Welding Applications: Case Studies and Skill Enhancement
7018 electrodes have garnered a reputation for their reliability and strength in various welding applications. From structural steelwork to intricate pipe joining, these electrodes have proven their mettle in numerous scenarios.
Structural Steel Applications with 7018 Electrodes
- Strength and Durability:
- 7018 electrodes are favored in structural steel projects due to their ability to create strong and tough welds. This is crucial in applications demanding high structural integrity, such as in building frameworks and infrastructure projects.
- Their low hydrogen content minimizes the risk of hydrogen-induced cracking, a critical factor in the longevity of steel structures.
- Case Study Insights:
- Studies and field reports consistently show that when 7018 electrodes are used correctly, they significantly enhance the longevity and safety of steel structures.
- For instance, in the construction of high-rise buildings, 7018 electrodes have been instrumental in ensuring the strength and resilience of key load-bearing joints.
Repair and Maintenance Welds with 7018 Electrodes
- Efficiency in Repairs:
- The 7018 electrode is a top choice for repair work, excelling in producing clean, crack-resistant welds. This is especially important in maintenance tasks where weld integrity can’t be compromised.
- Its efficacy on rusty or painted metals makes it a practical option for field repairs, reducing the need for extensive surface preparation.
- Practical Applications:
- In the maintenance of industrial machinery, 7018 electrodes have been used successfully to repair cracks and wear in high-stress components, prolonging their operational life.
- In the restoration of historical metal structures, these electrodes have provided reliable solutions for reinforcing weakened joints without causing further damage to the original materials.
Key Takeaways for 7018 Stick Welding Applications
- Versatility: The 7018’s ability to perform well in both pristine and less-than-ideal conditions makes it a versatile tool in the welder’s arsenal.
- Reliability: Whether it’s supporting the skeleton of a skyscraper or mending a critical machine part, the 7018 electrode has proven its reliability in maintaining structural integrity and safety.
- Best Practices: These case studies underscore the importance of following best welding practices, such as proper electrode storage and correct amperage settings, to fully leverage the benefits of 7018 electrodes.

I’ve been involved in the welding industry for over twenty years. I trained in various engineering shops working on various projects from small fabrication and repairs through to industrial projects.I specialize in welding aluminum and food grade stainless steel and an now run an engineering shop fabricating equipment for the food industry.